Act I
Initiation
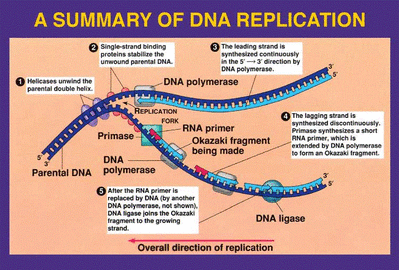
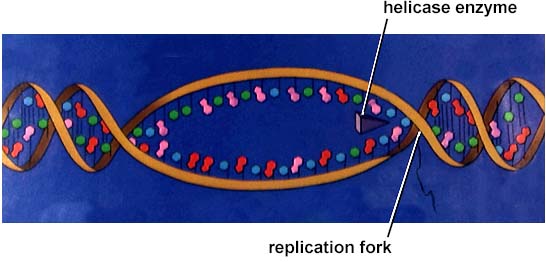
Helicase
splits/opens the template DNA strand at the replication fork = creation of
bubble
Single-strand binding proteins stabilize the unwound parental DNA , otherwise there is a risk the strands will bond back together
A lot of tension has built up , from parts of the DNA strands being straightened. The gyrase cuts the stands to release tension
RNA primase creates RNA primers that act as a starting point for replication
The DNA polymerase III recognize the primers
The parental strands are replicated in the direction of 5' to 3'
Leading strand- Polymerase III begins adding nucleotides to the RNA primer in the direction of the opening replication fork, it does this continuously
The lagging strand waits for enough of the replication fork to open ...... when it has opened sufficiently a DNA primer attaches to the parental strand and polymerase III makes a new starting point( discontinuous process)
The second strand is composed of Okazaki fragments ( 100-200 nucleotides long) and RNA primers

Lagging= discontinuous, RNA primers, Okazaki fragments , polymerase III
Leading= continuous, 1 Primer, Polymerase III
The two new strands are assembled in the opposite direction

Act III
Termination
Polymerase I removes the RNA nucelotides one at a time, replacing them with DNA nucleotides, this process is catalyzed by DNA ligase
Polymerase I and polymerase II( slow enzyme) are repair mechanisms, they work to repair damage done to DNA during replication, and proofread